What You Should Know About Bladder, Bone, Brain and Breast Cancer
Become educated about cancer – the risks, early detection methods, and prevention. Knowing the facts about cancer can save lives. What you eat and drink, how you live, where you work, all these factors can affect the risk for cancer and primary cancer prevention means taking the necessary precautions to prevent the occurrence of cancer.
Bladder Cancer
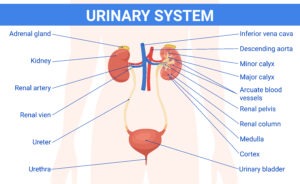
The bladder plays a very important role in the totality of our health. It functions as a reservoir for urine in our bodies. When the kidneys filter waste from the blood, urine is produced that enters into the bladder through two tubes called ureters, the bladder then allows the storage of urine for a period of time before being released in urination through another tube called urethra. The bladder can be thought of as a muscular balloon; a flattened structure when there is no urine (immediately after a person urinates) but can be filled up to a liter with urine. Normally when the bladder is filled with urine of about half a liter, we feel the urge to urinate. The muscular structure of the bladder also helps other pelvic muscles to push the urine out when released. The bladder is located in the lower abdomen deep in the pelvis, just above the pubic symphysis.
Bladder cancer refers to any of several types of malignant growth of the urinary bladder. It is a disease in which abnormal cells multiply without control in the bladder. The greatest risk factor for bladder cancer is genetic predisposition (a genetic effect that influences the phenotype of an organism but which can be modified by the environmental conditions); it can also be linked with smoking and occupational exposure to aniline-based dyes (such as textile factory), as well as with petrol and other chemicals.
The most common warning sign of bladder cancer is the presence of blood in the urine, the colour can be faintly rusty to deep red depending on the amount of blood present. Other symptoms include pain during urination, frequent urination, or feeling the need to urinate without results. However, these signs and symptoms are not specific to bladder cancer, but may also be caused by non-cancerous conditions such as prostate infections and cystitis. When symptoms do occur, see the doctor right away as any illness should be diagnosed and treated as early as possible.
What are the treatments for bladder cancer?
The treatment of bladder cancer depends on how deep the tumor invades into the bladder wall.
Superficial Bladder Cancer Treatment
This is when the cancer has not invaded into the muscle at all and can be “shaved off” using an electrocautery device attached to a cystoscope. As superficial bladder cancer has high incidence of recurrence, the aim of treatment changes to prevent these recurrences and to prevent progression into an invasive stage. Immunotherapy, in the form of BCG instillation, is also used in the treatment and prevention of the recurrence of superficial tumors. Instillation of chemotherapy into the bladder can also be used to treat this disease.
Muscle Invading Bladder Cancer Treatment
Tumors that infiltrate the bladder require more radical surgery where part or the entire bladder is removed in a surgical removal procedure called cystectomy wherein the urinary stream is diverted. In some cases, skilled surgeons can create a substitute bladder (neobladder) from a segment of intestinal tissue, but the procedure vastly depends upon patient preference, renal function, and the site of the disease.
Bladder cancer is the sixth (6) most common cancer in men and the seventeenth (17) most common cancer in women. Globally, it is the 10th most common cancer. In 2020, there were more than 573,000 new cases.
Bone Cancer
Cancer of the bone or bone cancer is a general term used when cancer cells are seen in the bone. Cancer that begins in the bone is called primary bone cancer. It is found most often in the arms and legs but it can occur in any bone in the body. Children and young people are more likely than adults to have bone cancers.
Primary bone cancers are called sarcomas. There are several different types of sarcoma and each type begins in a different kind of bone tissue. The most common sarcomas are osteosarcoma, Ewing’s sarcoma, and chondrosarcoma.
In young people, the most common type of bone cancer is osteosarcoma, usually occurring between the ages of ten and twenty-five. More often, males are affected than females. Osteosarcoma frequently starts in the ends of the bones; where new bone tissue forms as a young person grows, usually affecting the long bones of the arms and legs. Ewing’s sarcoma usually affects teenagers, and is mostly found in people between ten and twenty-five years old. This cancer forms in the middle part (shaft) of large bones and most often affects the hip bones and long bones in the thigh and upper arm, but can also occur in the ribs. Chondrosarcoma is a type of tumor that forms in the cartilage (rubbery tissue around the joints) and are found mainly in adults. Other types of bone cancer include fibrosarcoma (malignant giant cell tumor) and chordoma. These are rare cancers and most often affects people over thirty.
The most common symptom of bone cancer is pain. However, symptoms may vary depending on the location and size of the cancer. Sometimes firm, slightly tender lump on the bone can be felt through the skin. Sometimes bone cancer interferes with normal movements and can also weaken or cause bones to break. Tumors that occur in or near joints may cause swelling and tenderness in the affected area. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, weight loss, and anemia. It is important to check with a doctor when you experience these symptoms, but these symptoms can also be caused by other less serious conditions.
Treatment for some bone tumors may involve surgery such as limb amputation. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are effective in some tumors (such as Ewing’s sarcoma) but less so in others (such as chondrosarcoma). After treatment has been done for bone cancer, it is very important that regular follow-up or check-ups are done with your doctor, to be sure that cancer has not come back and treat it promptly if it does. Check-ups may be physical exam, x-rays, scans, blood tests, and other laboratory tests.
People who have been diagnosed of bone cancer may have many physical, emotional, practical worries. They may worry that removal of a limb or other surgery will affect not only how they look but how other people would feel about them. Patients can be helped to overcome all these through special support groups for youngsters with cancer and their families.
Brain Cancer
The term brain cancer although often used by the general public is actually not the term often used by the medical community. Primary brain tumor is the term used by the medical community for tumors arising form the brain. In children, most brain tumors are primary tumors. In adults however, most tumors in the brain have spread from the lung, breast, or other parts of the body. When this happens, the disease is not brain cancer. The tumor in the brain is a secondary tumor and it is named after the organ or tissue fromch it began.
A brain tumor is any intracranial tumor created by abnormal and uncontrolled cell division, normally either found in the brain itself, in the cranial nerves, in the brain envelopes, skull, pituitary and pineal gland, or from cancers primarily located in other organs. Although they can affect any part of the brain, primary brain tumors in children are generally located in the posterior cranial fossil; and in adults, in the anterior two-thirds of the cerebral hemispheres.
The most common brain tumors or brain cancers are gliomas, which start in the glial (supportive) tissue. Several types of gliomas include astrocytomas, ependymomas, and oligodendrogliomas.
The development of certain types of primary brain tumors or brain cancers has been linked to exposure to radiation, especially if exposure took place in childhood. It is generally believed that higher radiation doses increase the risk of eventually developing a brain cancer. Radiation-induced brain tumors can take anywhere from ten to thirty years to form. The exposure to vinyl chloride and/or ionizing radiation are the only known risk factors; other than these there are no known environmental factors that can be associated with brain tumors. The so-called tumor suppressor genes mutations and deletions are incriminated in some forms of brain tumors. Inherited diseases such as Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome, neurofibromatosis type 2, and multiple endocrine neoplasia of a patient pose a high risk to having brain tumor.
Symptoms of brain tumor and brain cancer are caused by the damage to the vital tissue and by pressure on the brain as the tumor grows within the limited space in the skull. If a brain tumor grows very slowly, its symptoms may appear so gradually that they are sometimes overlooked for a long time. The most frequent symptoms of brain tumors or brain cancer include headache, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, seizures, memory loss, weakness, visual changes, problems with speech and language, personality changes, and thought processing problems. These symptoms may be caused by brain tumors or by other problems. If a person is experiencing such symptoms, consulting a doctor right away is strongly advised.
A person diagnosed with brain cancer or brain tumor will undergo treatments that include surgery (surgical resection), which is recommended for the majority of brain tumors. It is rare in primary brain tumor to be cured without a surgical resection. Other treatments include chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Breast Cancer
Globally, breast cancer is the most common cancer. In 2020 there were more than 2.26 million new cases. Previously, after lung cancer, breast cancer was the second most fatal cancer in women. However, now breast cancer is the main cancer in women. The breast is composed of identical tissues in males and females, that is why breast cancer can also occur in males but the incidence is very low, less than one percent.
What is breast cancer? Breast cancer occurs when the cells in the breast begin to grow uncontrollably and invade the nearby tissues or spread throughout the body. These extra cells can form a mass of tissue called a growth or tumor. Tumors can be benign or malignant. Benign tumors may grow larger but do not spread to other parts of the body, they are not cancerous. They are rarely life threatening, and generally benign tumors can be removed and don’t usually grow back. Malignant tumors on the other hand, can invade and destroy nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body, they are cancerous. They may be life threatening. They can be removed but they sometimes grow back. Cells from malignant tumors can spread to other parts of the body. Cancer cells spread by breaking away from the original or primary tumor and entering the bloodstream or lymphatic system. The cells invade other organs and form new tumors that damage these organs. The spread of cancer is called metastasis.
When breast cancer cells spread, they are often found in lymph nodes near the breast. Breast cancer can also spread to almost any part of the body; the most common are the bones, liver, lungs, and brain. This new tumor has the same kind of abnormal cells and the same primary tumor, which results to different types of cancer.
What are the risk factors of breast cancer? The exact cause of this disease cannot be determined but doctors often explain why one woman develops breast cancers and another does not. One thing is for sure, bumping, bruising, or touching the breast does not cause cancer. It is also not contagious. Research has shown that women with certain risk factors are more likely to develop the disease. Here are some risk factors for breast cancer:
Age. As a woman gets older the chances of getting the disease goes up.
Personal history of breast cancer. If a woman has had breast cancer on one of her breast, there is an increased rate of getting cancer on the other breast.
Family history. If a family member has had breast cancer, like the mother, sister or daughter, or other relatives (either the mother’s or father’s side) the risk of breast cancer is higher.
Certain Breast Changes. Some women have abnormal cells in the breast called, atypical hyperplasia and lobular carcinoma in situ, increases the risk of breast cancer.
Gene Changes. Changes in genes increases the risk of breast cancer, this includes BRCA1, BRCA2, and others.
Reproductive and Menstrual History. The older the woman is when she has her first child increases the chance of having the disease. Women who had their first menstrual period before age 12, women who went through menopause after age 55, women who never had children, women who take menopausal hormone therapy with estrogen plus progestin, have risk to having breast cancer.
Race. More often, breast cancer is diagnosed in white women than Latin, Asian, or African American women.
Other risk factors include: radiation therapy to the chest before age 30, breast density (more dense or fatty tissue are at increased risk), taking DES (diethylstilbestrol), being overweight or obese, lack of physical activity and alcohol. Other possible risk factors are under study, including certain substances in the environment.
What are the symptoms of breast cancer? Unfortunately, early stages of this disease may not have symptoms. Following screening recommendations or having regular breast check-ups is important. As a tumor grows in size, it produces a variety of symptoms that include:
- lump or thickening in the breast or underarm
- change in size or shape of the breast
- nipple discharge or nipple turning inward
- redness or scaling of the skin or nipple
- ridges or pitting of the breast skin
Having or experiencing these symptoms may not necessarily mean that you have breast cancer, but you need to be examined by a doctor. Early detection and treatment of the disease if diagnosed can save you from illness or maybe even death.
Other cancer articles you might like:
Who Else Wants a Diet That Lowers Your Risk of Cancer
A Cancer Survivor’s Guide to Returning to Work
What You Should Know About Cervical, Colon, Kidney and Liver Cancer

















































































